

*Ĝapnogram is the waveform displayed by the capnograph *Ĝapnography is the graphic representation of expired CO2 over time *Ĝapnometry is the measurement of expired CO2 and provides a numeric display of CO2 tension in mm Hg or %CO2.

,, Absent ETCO2 is found in oesophageal intubation. Decreased ventilation will increase PaCO2 and increase ETCO2-PaCO2 difference as in asthma, atelectasis, pneumonia and emphysema. So usually the net ETCO2 underestimates the PaCO2 in cases of v/q mismatch, such as shock, CPR, pulmonary embolism, etc. ,, , In non-perfused alveoli, the CO2 concentration is zero and in adequately perfused alveoli the CO2 concentration is normal. The v/q ratio is about 0.8, usually because there is some dead space (main airway and alveoli). ,, ,, ETCO2 represents PaCO2 from all ventilated alveoli and PaCO2 represents PaCO2 of all perfused alveoli. ,, ,, It is usually 2-5 mm Hg less than PaCO2. If ventilation (v) and perfusion (q) are well matched, the ETCO2 will nearly equal PaCO2. ,, ,, During shock or cardiac arrest, ETCO2 levels will be reflective of pulmonary blood flow and cardiac output and not minute ventilation.
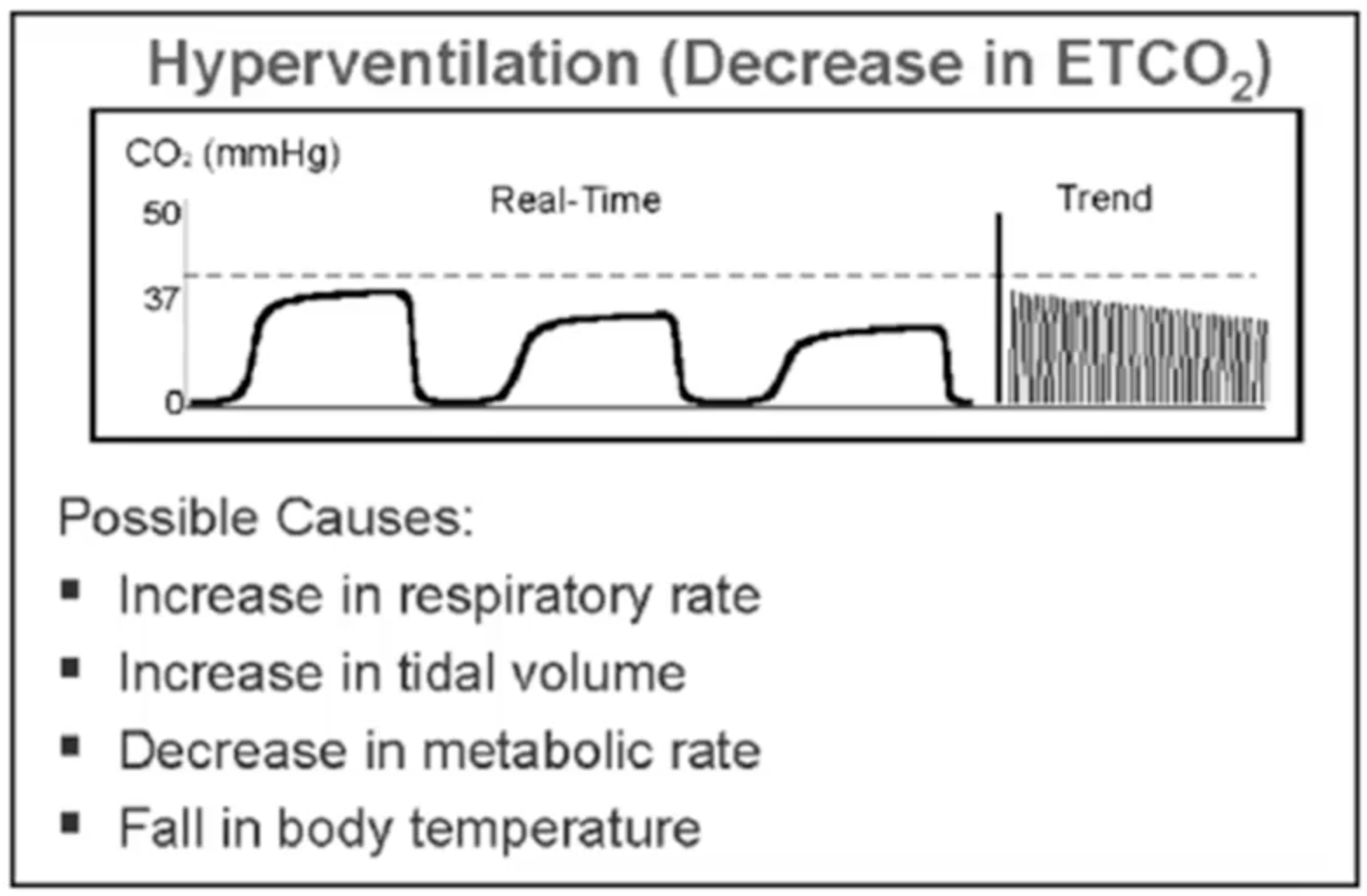
,, CO2 production normally remains constant, and when circulation is normal, ETCO2 usually changes with ventilation and therefore approximates PaCO2. ,, If any two systems are kept constant, then the changes in ETCO2 will reflect changes in the third system. ,, ETCO2, therefore, is a reflection of metabolism, circulation and ventilation. ,, It is then pumped into the lungs by the heart and then diffuses out into the exhaled air where it can be measured. A companion article will discuss the clinical applications in the paediatric emergency setting.ĬO2 is produced by cellular metabolism and is transported to the right heart by the venous system. This article will review the basic physiology, the technology, both qualitative and quantitative, and discuss capnograms. ,, It has become the standard of care in the operating room, ICU and now being increasingly used in the emergency department and the prehospital setting. ETCO2 monitoring has been a boon allowing us to measure exhaled CO2 non-invasively by different methods. PaCO2 (partial pressure of CO2 in the arterial blood) is a direct measurement of ventilation status but is invasive and the data are not continuous. Ĭritically ill children need to have their airways controlled by endotracheal intubation and their ventilation status optimally managed. This methodology was first studied clinically by Smallhout and Kalenda in the 1970s, studied extensively over the last 2 decades and now is being used extensively mainly to verify endotracheal tube (ETT) position and during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Available from: Įnd-tidal CO2 (ETCO2) monitoring allows exhaled CO2 to be measured non-invasively. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in pediatrics: concepts and technology. Hypocapnia/Hyperventilation 2 An ETCO₂ level lower than normal, less than 4.0 % (34 mmHg), is called hypocapnia.Keywords: Carbon Monoxide, analysis,Emergencies, Human, Monitoring, Physiologic, methods,Pediatrics, Tidal Volume, Kalenda, Mastering Infrared Capnography, p48, 1989 Spontaneous breathing can be instituted more easily by allowing the EtCO 2 rise at the end of the anesthesia and patient usually experiences a more rapid recovery.ĭuring lengthy anesthesia, there is typically a very gradual decrease in EtCO 2 due to the depressant effect of anesthetic agents and the effect of hypothermia slowing the patient’s metabolism.ġ Z. With normoventilation, disturbances in ventilation, circulation and metabolism can be more easily recognized and monitoring enables to maintain the physiologically optimal minute ventilation. ”carbia” refers to CO 2 level in the bloodĪlveolar minute ventilation is usually adjusted to achieve normocapnia, where EtCO 2 is in the range 4.0-6.Hypercapnia EtCO 2 more than 6.0 vol % 45 mmHg Common terms in CO 2 monitoring: Hypocapnia EtCO 2 less than 4.0 vol % 35 mmHg


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
